The Capacity Building Commission (CBC), established three years ago by the Indian government, has introduced the Karmayogi Competency Model — a comprehensive framework to guide civil servants in their professional development. This model aims to transform civil servants from karmacharis (mere employees) to karmayogis (dedicated public workers) by mapping their skills to the demands of modern governance.
The inspiration for this framework comes from Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s Mann Ki Baat radio broadcasts and his various public addresses. R Balasubramaniam, Member (Human Resource) of the CBC, highlighted that they conducted a large language model (LLM) analysis of the PM’s speeches, tweets, and other communications to distill core themes. Four guiding resolutions emerged — vikas (development), garva (pride), kartavya (duty), and ekta (unity) — forming the foundation for the model.
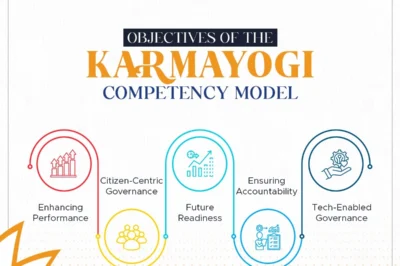
The Karmayogi Competency Model comprises 34 competencies, categorized into 13 ‘behavioural’ and 21 ‘functional’ attributes:
- Behavioural Competencies: These include self-awareness, creativity, strategic leadership, and personal effectiveness. They are divided into core and leadership competencies aimed at fostering personal growth and leadership qualities among civil servants.
- Functional Competencies: These focus on skills like citizen centricity, policy architecture, digital fluency, financial management, and data analytics — essential for effective public service in a digital and citizen-focused era.
The CBC has designed the model to address the challenges of modern governance, including increased accountability, technology-driven governance, and preparedness for unforeseen global events. “Today, civil servants are expected to go beyond just delivering schemes and act with a mindset of service,” said Balasubramaniam. This shift aligns with PM Modi’s vision of building a more dedicated and capable bureaucracy.
To facilitate this transition, civil servants will soon undergo competency assessments. Based on the results, an algorithm will recommend targeted courses through the Integrated Government Online Training (iGOT) portal. These courses are linked to the competencies required for various roles, enabling quick upskilling. Completion of the training will be tracked through the e-HRMS (Human Resource Management System), allowing supervisors to monitor their team’s skill development.
Currently, all government employees are mandated to complete at least 50 hours of training annually on the iGOT platform, with competencies directly influencing their job assignments. This structured approach allows civil servants to acquire new skills rapidly, particularly when faced with responsibilities that require upskilling.
The Karmayogi Competency Model was formulated through extensive research and consultations involving public and private sector representatives, academia, and experts in Indian Knowledge Systems. It also drew on global best practices, benchmarking against competency models from countries like Australia, Singapore, and South Korea.
The initiative currently targets civil servants at the Central government level, with state governments like Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh also participating. The CBC, which was founded in April 2021, has a unique structure, incorporating private sector and civil society representation alongside traditional bureaucratic leadership. Key figures include Adil Zainulbhai, former McKinsey India head as Chairperson, Balasubramaniam as Member (HR), and Alka Mittal, former CMD of ONGC, as Member (Administration).





































































Leave a Reply